Crystallins are water-soluble proteins that are necessary for sight as they focus light on the retina. Present in high concentrations, up to 450 mg/mL in the human lens, these proteins do not undergo protein turnover and, as such, must be extremely soluble and thermodynamically stable. J2-crystallin is a novel eye lens protein that is highly expressed in Tripedalia cystophora (box jellyfish). Unlike most non-cephalopod invertebrates, box jellyfish have camera-type eyes; therefore their crystallins present an interesting system from an evolutionary biology perspective, making them an intriguing model system for vertebrates. Tripedalia cystophora has 24 eyes total that are split among four rhopalia, or sensory structures, around the bell of the organism. Each rhopalium contains two camera-type eyes placed at a right angle from one another, two pit-shaped pigment cup eyes, and two slit-shaped pigment cup eyes allowing for a complete view of its surroundings. Of the pair of camera-type eyes in each rhopalium, one is larger than the other. The camera-type eye lenses contain three crystallins known as J1-crystallin, found in both the large and small eyes, and J2- and J3-crystallins, found only in the large eye.
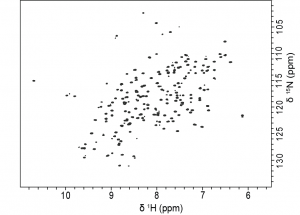
J1- and J3-crystallins are homologous to well-known enzymes, S-crystallins and saposins, respectively, whereas J2-crystallin has no known homologs. Having no known homologs, this protein has not been previously studied and potentially represents a novel fold. Our lab is interested in the biophysical characterization solution NMR structure for J2-crystallin by using optical and NMR spectroscopic methods.
